Bubble echo
Bubble echo
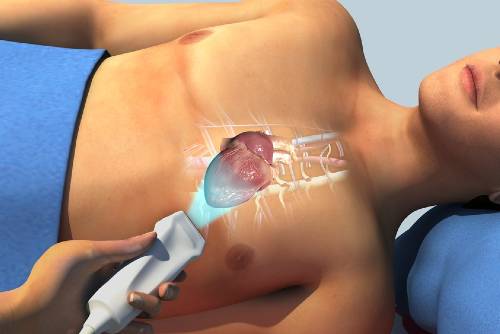
What it is and how it works: A bubble echocardiogram is a test that involves injecting salt (saline) water bubbles into the blood stream to see whether they stay within the correct side of the heart or not. A normal heart should retain the bubbles within the right chamber (atrium). If the bubbles leak into the left side, this indicates that there might be a structural problem with the heart. During the test, a small drip containing the saline bubbles will be attached to your arm. You will also be connected to an ECG. An ultrasound will be applied to your chest to help take images of your heart. Once the saline bubbles have been injected, your doctor will observe how the solution fills the heart. Usually, the test takes around 30 minutes.
What it detects: A bubble echocardiogram is a test to help diagnose a patent foramen ovale or an atrial septal defect. These are also referred to as congenital heart defects.